GLM-ASR-Nano-2512
👋 Join our WeChat community
Model Introduction
GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 is a robust, open-source speech recognition model with 1.5B parameters. Designed for real-world complexity, it outperforms OpenAI Whisper V3 on multiple benchmarks while maintaining a compact size.
Key capabilities include:
Exceptional Dialect Support: Beyond standard Mandarin and English, the model is highly optimized for Cantonese (粤语) and other dialects, effectively bridging the gap in dialectal speech recognition.
Low-Volume Speech Robustness: Specifically trained for "Whisper/Quiet Speech" scenarios. It captures and accurately transcribes extremely low-volume audio that traditional models often miss.
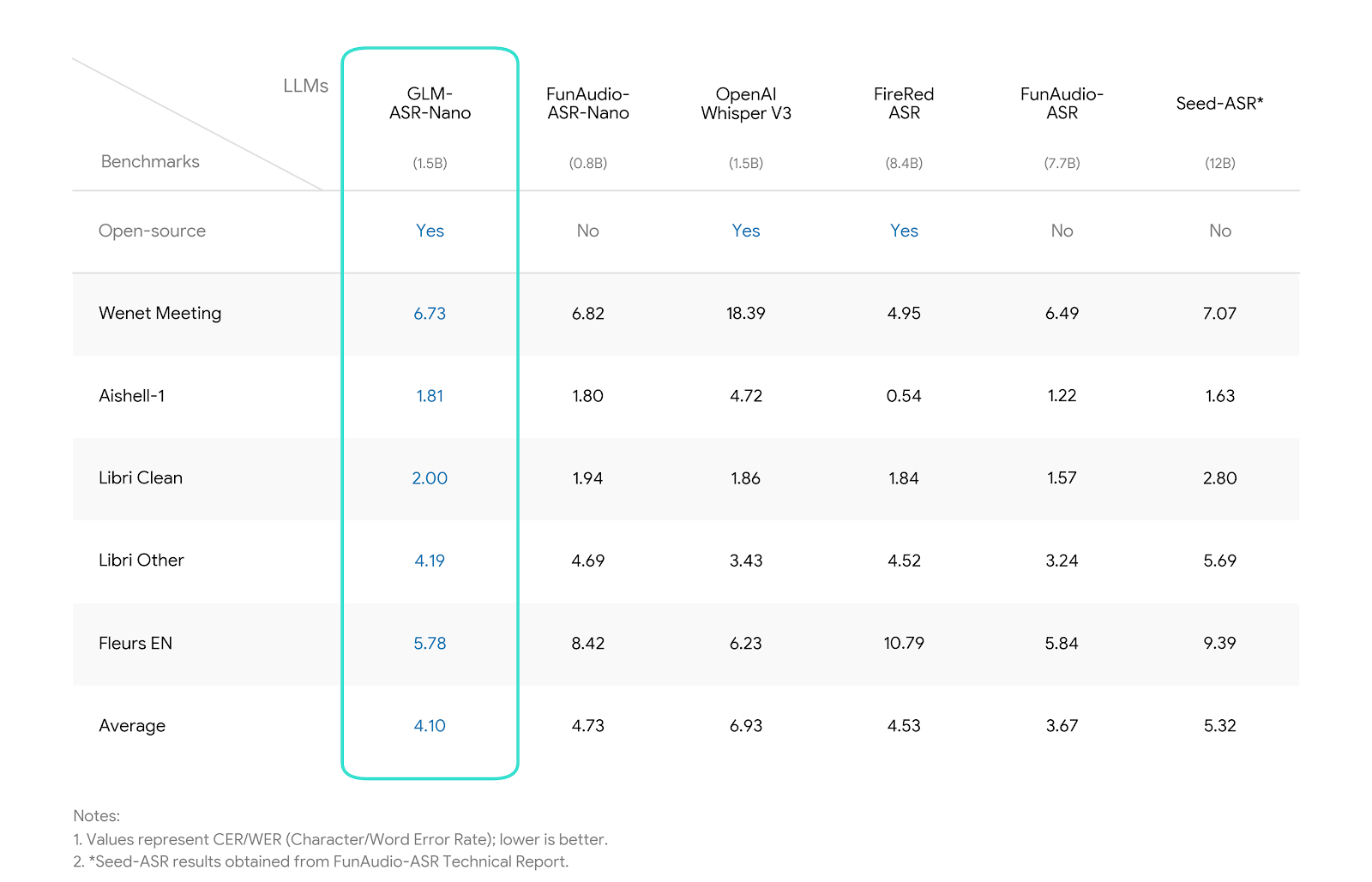
SOTA Performance: Achieves the lowest average error rate (4.10) among comparable open-source models, showing significant advantages in Chinese benchmarks (Wenet Meeting, Aishell-1, etc..).
Benchmark
We evaluated GLM-ASR-Nano against leading open-source and closed-source models. The results demonstrate that * GLM-ASR-Nano (1.5B)* achieves superior performance, particularly in challenging acoustic environments.
Notes:
- Wenet Meeting reflects real-world meeting scenarios with noise and overlapping speech.
- Aishell-1 is a standard Mandarin benchmark.
Inference
GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 can be easily integrated using the transformers library.
We will support transformers 5.x as well as inference frameworks such as vLLM and SGLang.
you can check more code in Github.
Transformers 🤗
Install transformers from source:
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
Basic Usage
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoProcessor
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512")
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512", dtype="auto", device_map="auto")
inputs = processor.apply_transcription_request("https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/dummy-audio-samples/resolve/main/bcn_weather.mp3")
inputs = inputs.to(model.device, dtype=model.dtype)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, do_sample=False, max_new_tokens=500)
decoded_outputs = processor.batch_decode(outputs[:, inputs.input_ids.shape[1] :], skip_special_tokens=True)
print(decoded_outputs)
Using Audio Arrays Directly
You can also use audio arrays directly:
from transformers import GlmAsrForConditionalGeneration, AutoProcessor
from datasets import load_dataset
from datasets import Audio
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512")
model = GlmAsrForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512", dtype="auto", device_map="auto")
# loading audio directly from dataset
ds = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/librispeech_asr_dummy", "clean", split="validation")
ds = ds.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=processor.feature_extractor.sampling_rate))
audio_array = ds[0]["audio"]["array"]
inputs = processor.apply_transcription_request(audio_array)
inputs = inputs.to(model.device, dtype=model.dtype)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, do_sample=False, max_new_tokens=500)
decoded_outputs = processor.batch_decode(outputs[:, inputs.input_ids.shape[1] :], skip_special_tokens=True)
print(decoded_outputs)
Batched Inference
You can process multiple audio files at once:
from transformers import GlmAsrForConditionalGeneration, AutoProcessor
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512")
model = GlmAsrForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512", dtype="auto", device_map="auto")
inputs = processor.apply_transcription_request([
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/dummy-audio-samples/resolve/main/bcn_weather.mp3",
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/dummy-audio-samples/resolve/main/obama.mp3",
])
inputs = inputs.to(model.device, dtype=model.dtype)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, do_sample=False, max_new_tokens=500)
decoded_outputs = processor.batch_decode(outputs[:, inputs.input_ids.shape[1] :], skip_special_tokens=True)
print(decoded_outputs)
- Downloads last month
- 442,289